Notifications
ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR SHAMPOO
1.PHYSICAL APPEARANCE/VISUAL INSPECTION
The formulations were evaluated in terms of their clarity, color, odor and texture.
2. DETERMINATION OF PH
PH of your 10% shampoo solution. Dip one strip of pH paper in the solution and compare the color of the strip to key. pH meter can also be used after calibration.
Most shampoos are neutral or slightly acidic. Acidic solutions cause the cuticle (outer layer) of the hair to shrink and lay flatter on the shaft of the hair. Basic solutions cause the cuticle to swell and open up. Acidic solutions make the hair seem smoother. Basic solutions make hair seem frizzier.
Neutral pH = 7 Acidic pH < 7 Basic pH >7
3. DIRT DISPERSION
Two drops of shampoo were added in a large test tube contain 10 ml of distilled water. 1 drop of India ink was added; the test tube was stoppered and shakes it ten times. The amount of ink in the foam was estimated as None, Light, Moderate, or Heavy.
Shampoos that cause the ink to concentrate in the foam are considered poor quality. The dirt should vstay in the water portion. Dirt that stays in the foam will be difficult to rinse away. It will redeposit on the hair.
4. DETERMINATION OF PERCENTAGE SOLID CONTENT
A clean dry evaporating dish was weighed and added 4 grams of shampoo to the evaporating dish. The dish and shampoo was weighed. The exact weight of the shampoo was calculated only and put the evaporating dish with shampoo was placed on the hot plate until the liquid portion was evaporated. The weight of the shampoo only (solids) after drying was calculated. If a shampoo has too many solids it will be hard to work into the hair or too hard to wash out. If it doesn’t have enough it will be too watery and wash away quickly. A good shampoo will be between 20% – 30% solids.
5. SURFACE TENSION MEASUREMENT
Measurements were carried out with a 10% shampoo dilution in distilled water at room temperature. Thoroughly clean the stalagmometer using chronic acid and purified water Because surface tension is highly affected with grease or other lubricants. The data calculated by following equation given bellow:
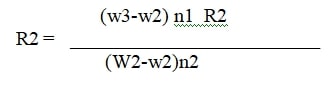
where W1 is weight of empty beaker.
W2 is weight of beaker with distilled water.
W3 is Weight of beaker with shampoo solution.
n1 is no. of drops of distilled water.
n2 is no. of drops of shampoo solution.
R1 is surface tension of distilled water at room temperature.
R2 is surface tension of shampoo solution
6. CLEANING ACTION
5 grams of wool yarn were placed in grease, after that it was placed in 200 ml. of water containing 1 gram of shampoo in a flask. Temperature of water was maintained at 350C. The flask was shaked for 4 minutes at the rate of 50 times a minute.
The solution was removed and sample was taken out, dried and weighed. The amount of grease removed was calculated by using the following equation:
DP = 100 (1-T/C)
In which, DP is the percentage of detergency power, C is the weight of sebum in the control sample and T is the weight of sebum in the test sample.
7. WETTING TIME
The canvas was cut into 1 inch diameter discs having an average weight of 0.44 g. The disc was floated on the surface of shampoo solution of 1% w/v and the stopwatch started. The time required for the disc to begin to sink was measured acutely and noted as the wetting time.
8. FOAMING ABILITY AND FOAM STABILITY
Cylinder shakemethod was most widely used for determining foaming ability. 50 ml of the 1% shampoo solution was put into a 250 ml graduated cylinder and covered the cylinder with hand and shaken for 10 times. The total volumes of the foam contents after 1 minute shaking were recorded. The foam volume was calculated only. Immediately after shaking the volume of foam at 1 minute intervals for 4 minutes were recorded